SquareX and Perplexity Dispute Alleged Comet Browser Vulnerability

Security researchers from SquareX and AI company Perplexity are engaged in a public dispute over a reported critical vulnerability in Perplexity's Comet AI browser. While SquareX claims the flaw could enable remote code execution without user consent, Perplexity has dismissed the research as "fake" while quietly implementing fixes.
The Vulnerability
SquareX, a browser security firm, published findings on what it describes as a critical vulnerability in Comet's architecture. The issue centers on an undocumented MCP API (chrome.perplexity.mcp.addStdioServer) and two embedded extensions—Agentic and Analytics—that users cannot disable.
MCP (Model Context Protocol) typically connects AI applications to external data sources. In Comet, the Agentic extension performs automated tasks, while Analytics collects browser data and monitors Agentic's activities.
Per SquareX's analysis, both extensions interact exclusively with perplexity.ai subdomains, and API access is restricted to those domains. However, the MCP API can bypass the browser's sandbox and execute commands on the device without requesting user permission.
According to the researchers, if an attacker compromised the perplexity.ai domain or the Agentic extension, they could potentially deploy ransomware, monitor user activity, or exfiltrate data.
Proof of Concept
SquareX demonstrated an attack using extension stomping: they created a malicious extension masquerading as the legitimate Analytics extension and used it to command Agentic to call the MCP API. The researchers successfully executed WannaCry ransomware on a test system.
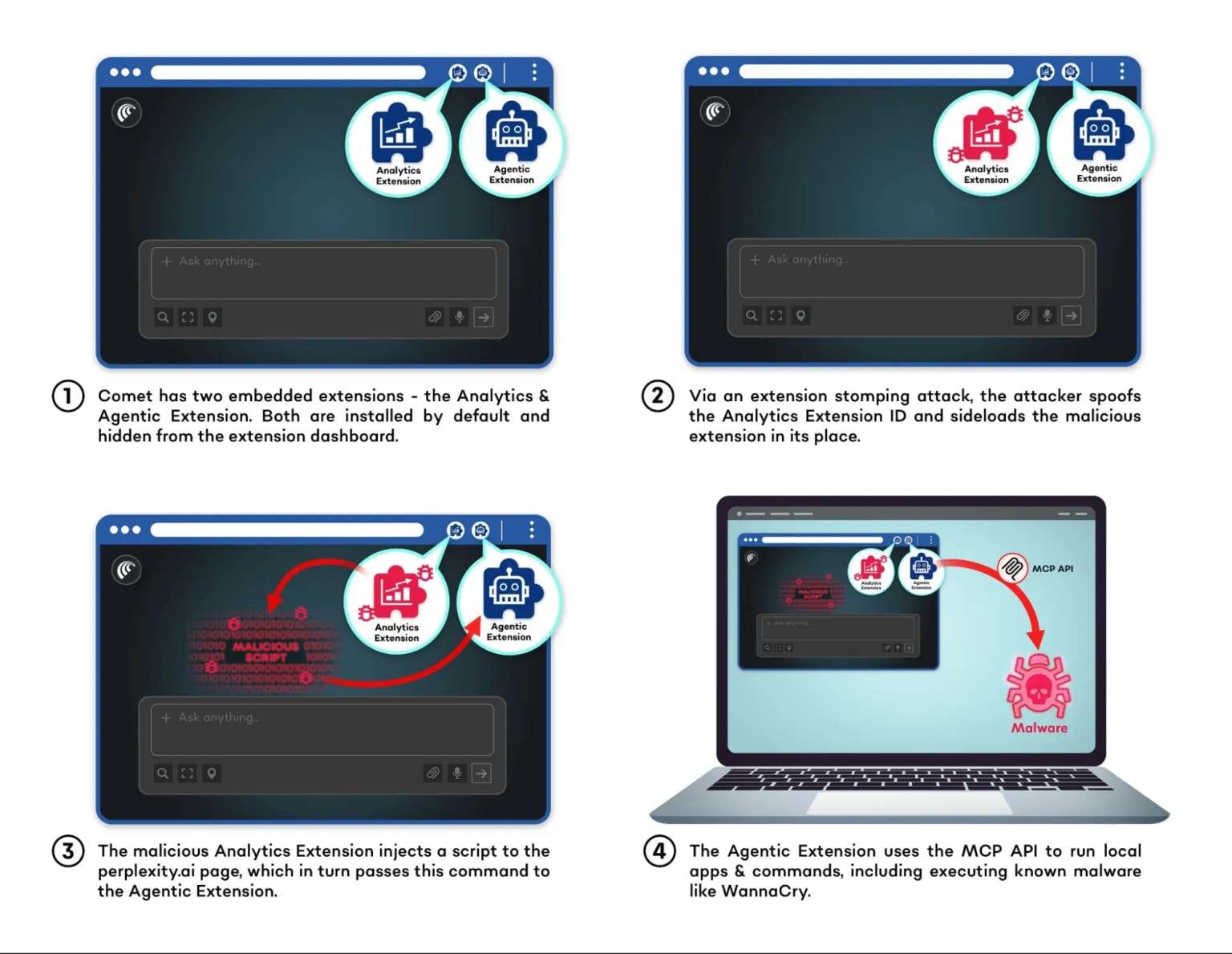
The security firm emphasized that other attack vectors—including cross-site scripting (XSS), man-in-the-middle attacks, or supply chain compromise—would require less user interaction. A breach of Perplexity's infrastructure would create immediate risk for all Comet users, they argued.
The Dispute
SquareX reported the vulnerability to Perplexity on November 4, 2025, but received no initial response. However, Perplexity representatives told media outlets they had already implemented protective measures while characterizing the research as fundamentally flawed.
"The entire scenario is artificial and does not represent a real risk. If it is a risk at all, it is a phishing risk where people are tricked into manually downloading malware. Even SquareX admits this is unrealistic and that replacing an existing extension with a malicious one would require a Perplexity employee with access to production resources," a company spokesperson stated.
Perplexity noted that SquareX's demonstration required significant manual intervention and that installing local MCPs and executing commands require user confirmation. The company also claimed it never received formal access to SquareX's report and that the researchers did not respond to requests for detailed vulnerability information.
Resolution
SquareX confirmed to journalists that Perplexity quietly patched the vulnerability in recent days without public disclosure. The demonstrated attacks no longer function, instead displaying the error "Local MCP is not enabled."
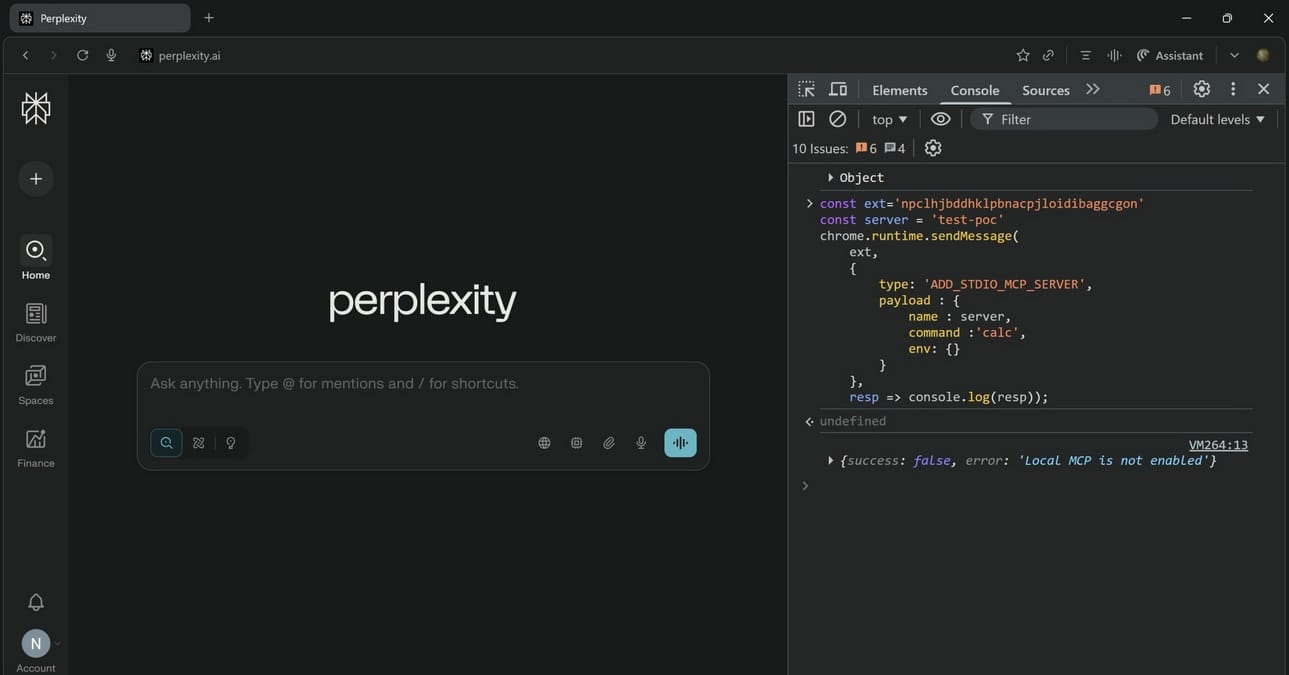
"This is great news, and we are glad that our research helped make the AI browser safer," SquareX representatives stated.