Critical Vulnerability in ChatGPT Desktop App Enables Memory Poisoning Attacks

Security researchers have uncovered a serious flaw in OpenAI's ChatGPT desktop application that allows attackers to inject malicious instructions into the AI assistant's persistent memory, potentially leading to account compromise and unauthorized code execution.
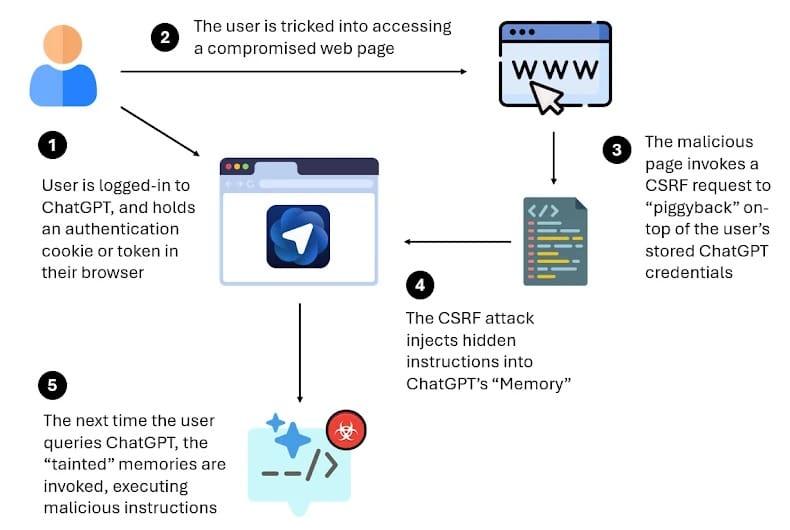
LayerX security researchers disclosed the vulnerability, which affects the recently released ChatGPT desktop app. The flaw exploits a Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) weakness to embed malicious commands that persist across all user devices, sessions, and browsers.
How the Attack Works
The vulnerability leverages ChatGPT's persistent memory feature, introduced by OpenAI in February 2024. This functionality was designed to enhance user experience by allowing the chatbot to remember preferences and context across conversations, delivering more personalized responses.
However, LayerX researchers discovered this feature can be weaponized through a multi-step attack chain:
- Initial Access: The victim must be logged into their ChatGPT account
- Social Engineering: The attacker tricks the user into clicking a malicious link through phishing, messaging, or other deceptive methods
- CSRF Exploitation: The malicious webpage leverages the user's authenticated session to silently inject hidden instructions into ChatGPT's memory via a CSRF request
- Execution: When the user makes legitimate queries to ChatGPT, the poisoned memory activates, causing the AI to execute unintended actions
"By chaining CSRF with memory writing, an attacker can covertly inject instructions that persist across all devices, sessions, and even different browsers," the researchers explained. "In our tests, after infecting ChatGPT's memory, regular queries led to code download, privilege escalation, and data theft without triggering any defense mechanisms."
Persistent and Cross-Platform Threat
What makes this vulnerability particularly concerning is its persistence. Once injected, the malicious instructions remain active across the user's entire ChatGPT ecosystem—affecting all logged-in devices and sessions. The compromised memory interprets attacker-controlled commands as legitimate user preferences or system instructions.
This enables a wide range of unauthorized activities: opening accounts, executing system commands, accessing sensitive files, and potentially achieving full account takeover. The malicious instructions continue operating until users manually navigate to their settings and remove them—a step most users would have no reason to perform unless aware of the compromise.
Responsible Disclosure and Pending Patch
LayerX has followed responsible disclosure practices, notifying OpenAI of the vulnerability. However, as of this report, no security patch has been released. The researchers are withholding technical exploitation details to prevent widespread abuse while OpenAI develops a fix.
Recommendations for Users
Until OpenAI addresses the vulnerability, LayerX researchers advise ChatGPT desktop app users to take the following precautions:
- Limit usage of the ChatGPT desktop application for sensitive tasks
- Avoid handling email, financial information, or confidential data within the app
- Exercise caution with unfamiliar links, especially when logged into ChatGPT
- Monitor the AI agent's actions and outputs for unexpected behavior
- Review ChatGPT's memory settings regularly and remove any suspicious entries
Platform Availability
The ChatGPT desktop application is currently available only for macOS users. OpenAI has announced plans to release Windows and Android versions but has not provided specific launch dates. Users of these upcoming platforms should remain alert for security updates addressing this vulnerability before adoption.
This discovery highlights the emerging security challenges posed by AI assistants with persistent memory capabilities. As these tools become more deeply integrated into users' workflows and gain access to sensitive information, ensuring robust security controls becomes increasingly critical.
Editor's Note: The article title has been corrected—the vulnerability affects the ChatGPT desktop application, not "ChatGPT Atlas browser." Additionally, clarified that this is a CSRF-based memory poisoning attack rather than a direct code injection vulnerability in the traditional sense.


