Critical Triofox Vulnerability Exploited: Hackers Deploy Remote Access Tools via Antivirus Feature

Google researchers have issued a warning: attackers are actively exploiting a critical vulnerability in Gladinet Triofox to execute remote code with SYSTEM privileges, bypassing authentication and seizing full control of systems.
The Vulnerability
The flaw, designated CVE-2025-12480, carries a CVSS score of 9.1 and stems from flawed access control logic. The system grants administrative privileges if a request appears to originate from localhost. This design choice allows attackers to forge the HTTP Host header and infiltrate systems without needing a password, according to experts from the Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG).
The problem becomes more serious when administrators fail to configure the optional TrustedHostIp parameter in web.config. Without this setting, the localhost check serves as the only security barrier, leaving default installations exposed to attack.
Gladinet released a patch for CVE-2025-12480 in version 16.7.10368.56560 on July 26th. Google experts confirmed with the vendor that the update resolves the issue.
Active Exploitation Observed
Despite the patch, security specialists are already tracking malicious activity exploiting this vulnerability. In August, a hacker group identified as UNC6485 targeted Triofox servers running the outdated version 16.4.10317.56372.
The attack demonstrated creative abuse of Triofox's built-in features. The threat actors sent a GET request with localhost in the HTTP Referer header, gaining access to the AdminDatabase.aspx configuration page—a component that runs during post-installation setup. The attackers then created a new Cluster Admin administrator account and uploaded a malicious script.
Weaponizing the Antivirus Feature
In a particularly clever twist, the hackers reconfigured Triofox to treat their malicious script as the location for the antivirus scanner. This manipulation caused the file to inherit the privileges of the parent Triofox process, executing it in the context of the SYSTEM account.
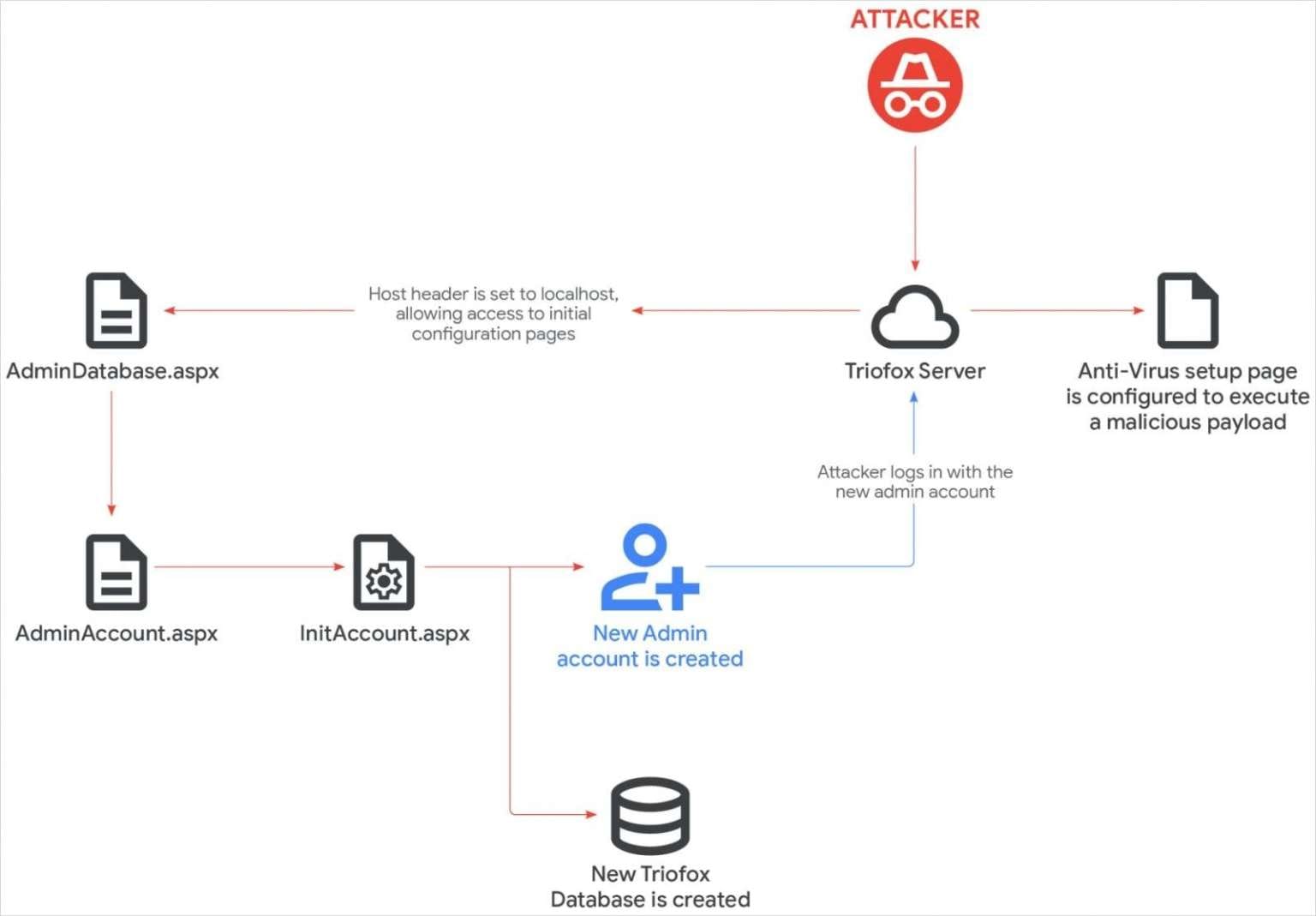
The script functioned as a PowerShell loader, downloading the Zoho UEMS installer. Using Zoho UEMS, the attackers deployed both Zoho Assist and AnyDesk for remote access and lateral movement across the network. They also leveraged Plink and PuTTY to establish SSH tunnels to the host's RDP port (3389).
Recommendations
Security experts recommend the following actions:
- Update Triofox immediately to version 16.10.10408.56683 (released October 14th) or later
- Audit all administrator accounts for suspicious or unauthorized entries
- Verify that the built-in antivirus is not executing any unauthorized scripts
- Configure the
TrustedHostIpparameter inweb.configto add an additional security layer
Organizations running Triofox should treat this as a priority security update, particularly if they cannot confirm that systems are running the patched version.


