Critical React Vulnerability Achieves Perfect 10 CVSS Score, Enables Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution
A critical vulnerability in React has received a perfect 10.0 CVSS score, allowing attackers to execute code remotely on servers without authentication. The flaw, tracked as CVE-2025-55182 and dubbed "React2Shell," threatens millions of applications built on React and Next.js frameworks.
React, Meta's open-source JavaScript library for building user interfaces, powers applications at Airbnb, Netflix, and thousands of other organizations. The main React npm package alone sees approximately 55.8 million weekly downloads. Next.js, a popular React-based framework, follows with 16.7 million weekly downloads.
How the Vulnerability Works
The flaw exists in how React processes data received through React Server Function endpoints. Attackers can send specially crafted HTTP requests to any Server Function endpoint, triggering malicious JavaScript code execution during deserialization. No authentication or elevated privileges are required.
New Zealand cybersecurity researcher Lachlan Davidson discovered the vulnerability and reported it to Meta developers on November 29, 2024. Davidson launched a dedicated website for React2Shell where technical details are published.
Per Endor Labs specialists, React2Shell stems from logically unsafe deserialization. The server cannot properly validate the structure of incoming React Server Component (RSC) payloads. When manipulated data arrives from an attacker, validation fails, leading to privileged JavaScript code execution in the server context.
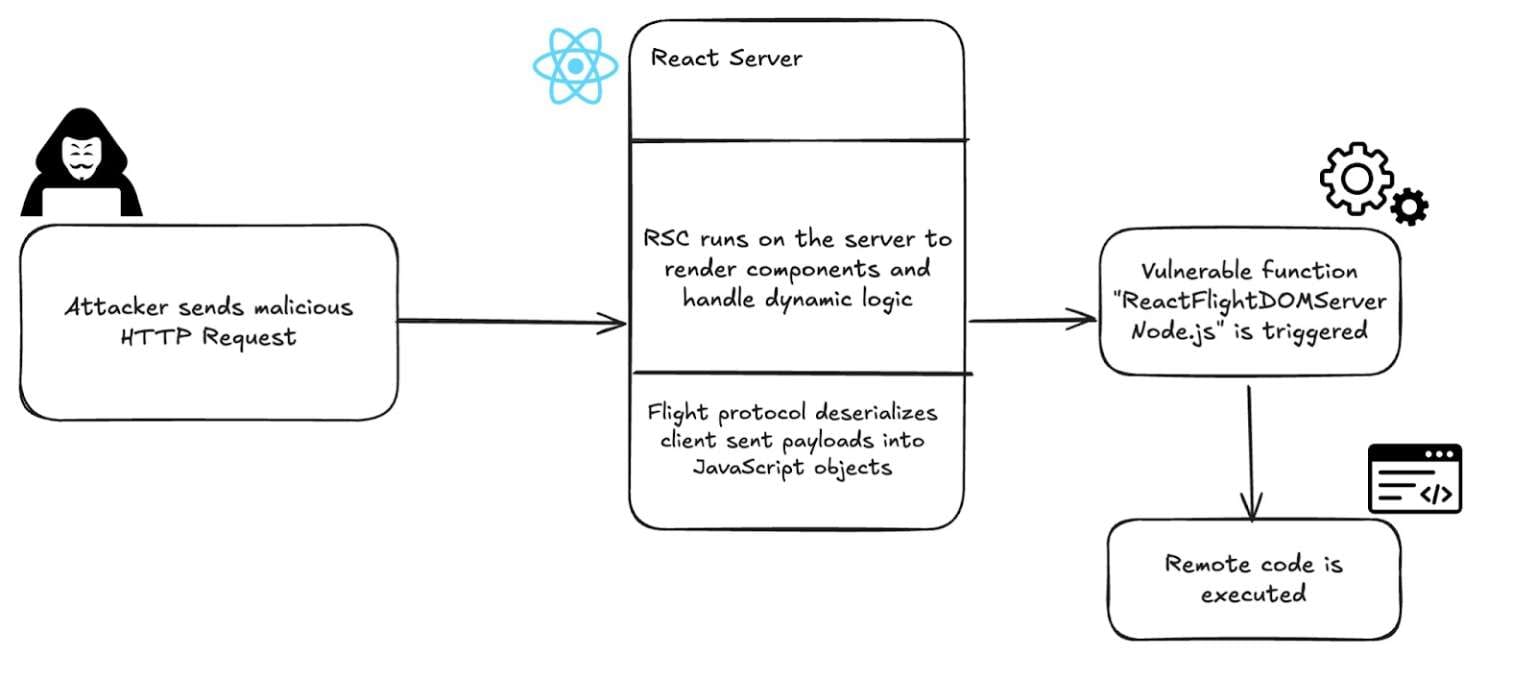
The vulnerability exploits default framework settings, meaning standard deployments are vulnerable without requiring special configurations. Researchers emphasize that attacks require only network access—no special permissions or unusual setups.
Affected Versions and Patches
CVE-2025-55182 affects the following npm packages in versions 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, and 19.2.0:
- react-server-dom-webpack
- react-server-dom-parcel
- react-server-dom-turbopack
React developers released fixes in versions 19.0.1, 19.1.2, and 19.2.1.
Next.js faces the same vulnerability. Vercel, the company behind Next.js, attempted to assign CVE-2025-66478, but NIST rejected it as a duplicate. Affected versions include canary releases starting from 14.3.0-canary.77 and all 15.x and 16.x branch releases below patched versions.
Patches are available for Next.js versions 16.0.7, 15.5.7, 15.4.8, 15.3.6, 15.2.6, 15.1.9, and 15.0.5.
Security specialists warn that other libraries implementing React Server functionality likely contain the same vulnerability, including:
- Vite RSC plugin
- Parcel RSC plugin
- React Router RSC preview
- RedwoodSDK
- Waku
React developers issued a warning in their security bulletin: "Even if your application does not implement React Server Function endpoints, it may still be vulnerable if it supports React Server Components (RSC)."
Scale of Exposure
Per Wiz, approximately 39% of all cloud environments contain instances vulnerable to CVE-2025-55182 or CVE-2025-66478.
Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 expert Justin Moore describes React2Shell as a universal "master key" that exploits the system's trust in incoming data rather than breaking the system itself. Over 968,000 servers using React and Next.js frameworks have been identified as potentially vulnerable.
Cybersecurity researcher Kevin Beaumont notes that the vulnerability is limited to React version 19 and only affects applications using the relatively new React Server functionality, which may reduce actual exposure compared to initial estimates.
BI.ZONE estimates that between 10,000 and 25,000 Russian web resources could be vulnerable, including small business sites and contractor services.
Industry Response and Exploit Activity
No confirmed exploitation of React2Shell has been reported in production environments. However, within 24 hours of public disclosure, at least one proof-of-concept exploit appeared online, and the vulnerability was added to various security scanners.
Davidson warned about fake proof-of-concept exploits circulating online. These fraudulent PoCs use functions like vm#runInThisContext, child_process#exec, and fs#writeFile, but authentic exploits do not require these functions. The fake PoCs do not work with Next.js because those functions are not present in that environment.
Major cloud and security providers responded rapidly:
Cloudflare deployed protection in Cloud WAF, automatically protecting all customers whose React application traffic is proxied through the service.
AWS, Akamai, Fastly, and Google Cloud implemented similar protective measures.
F5 is evaluating the potential impact on its products but has not identified any affected products yet.
Recommendations for Organizations
Security experts predict mass exploitation is not a matter of "if" but "when," given the vulnerability's severity and widespread use of affected frameworks.
Organizations should take immediate action:
- Update immediately - Apply patches for React (19.0.1, 19.1.2, 19.2.1) and Next.js (16.0.7, 15.5.7, 15.4.8, 15.3.6, 15.2.6, 15.1.9, 15.0.5)
- Deploy WAF rules - Until patches are installed, implement web application firewall rules to block suspicious requests
- Monitor traffic - Watch HTTP traffic to Server Function endpoints for unusual or malicious requests
- Restrict network access - If possible, temporarily limit network access to affected applications
- Audit environments - Conduct thorough audits to identify all instances running vulnerable versions
- Check dependencies - Verify whether other React Server implementations in your environment (Vite RSC, Parcel RSC, React Router RSC, RedwoodSDK, Waku) are affected
Organizations using React 19 or Next.js should treat this vulnerability as a critical priority. The combination of maximum CVSS scoring, no authentication requirement, and widespread framework adoption creates significant risk for unpatched systems.
Technical Details:
- CVE ID: CVE-2025-55182 (React), CVE-2025-66478 (Next.js, rejected as duplicate)
- CVSS Score: 10.0 (Critical)
- Attack Vector: Network
- Authentication Required: None
- Privileges Required: None
- Discoverer: Lachlan Davidson
- Disclosure Date: December 2024
- Patch Status: Available for all affected versions


